

Cultivation of Paulownia is exceptionally profitable business and it is gaining momentum every year! Not for nothing is it called a “miracle tree” or “tree-oil well”. If you have a desire to industrially grow Paulownia, to engage in gardening or simply you want to learn more about the miracle tree, about its features and proper cultivation, then you are on the right track!
HISTORICAL NOTES
Paulownia is a unique species of fast-growing trees that have no analogues in the world. On the pages of our site you will be able to find out everything that concerns the culture of Paulownia, and also to purchase our products.
The tree comes from China. The earliest documents and chronicles mentioning the use of this wonderful tree date back to 2,600 years AD. For centuries the tree grew in Japan. And it was known by the name of Kiri, which means “life” in Japanese. Kiri has always been considered a sacred tree and a symbol of good luck. By tradition, at the birth of a daughter in the family, they planted the Paulownia tree. When the girl got married, the tree was cut and her wedding trunk was made from it. In addition, there was such a belief that if you plant Paulownia near your home, the phoenix bird will fly and bring happiness.
In Japan, Paulownia has been used since 200 AD, and it represents a national value. The Japanese, who are very fond of both aesthetics and symbolism, chose Paulownia as an emblem in the cabinet of the minister (Fig. 1)
There is hardly a more explicit way to emphasize the national importance of Paulownia for the Japanese people than its presence in the Order of the Rising Sun (Fig.2). This first order of Japan was established in 1875, which was awarded to individuals of the highest rank, such as admirals, generals, diplomats, lawyers and politicians for their services to the country.
Also, Paulownia is depicted on a Japanese coin in the value of 500 yen (Fig.3).

In 1823, Philip Franz von Siebold, the German naturalist, visited Japan. After spending some time in Japan, he returned to Holland and brought with him the seeds of the beautiful Kiri. How to name this new beautiful plant? Of course, in honor of the beloved Queen of Netherlands, nee Romanova, the sixth daughter of Paul the First and Empress Maria Fedorovna. To name the species of the plant “Anna” was impossible, because this species already existed, and then it was decided to use for the name the patronymic of Anna, which was adopted for the second name – “Paulownia” in accordance with European way.
Anna Pavlovna helped a German naturalist finance an expedition to Southeast Asia. Later, together with Josef Zuccarini, he published the book Flora Japónica, where the properties and qualities of the tree were described for the first time ever. The Japanese liked the European name, and they also began to call this beautiful tree – Paulownia.
In China, Paulownia is grown on an area of 2.5 million hectares of which on 1.3 million hectares the cultivation of Paulownia is carried out in a combined way. In the spaces between rows such crops as cotton, corn, tea and other crops are planted.
Perhaps you have met this beautiful tree with its huge leaves and graceful, fragrant flowers in the city park. But you would never have thought that this beauty brings not only aesthetic pleasure, but also it has many useful qualities and properties.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION

Paulownia (Latin Paulowania), or Adam’s tree or the Tree of Life (Japan, Kiri) is a genus of the plants of the family Paulowniaceae, and it contains more than 20 species that have similar qualities and therefore they are called the collective name Paulownia (Latin Paulowania): P. australis, P. catalpifolia, P. coreana, P. duclouxii, P. elongate, P. fargesii, P. fortune, P. glabrata, P. grandifolia, P. imperialis, P. kawakamii, P. lilacina, P. longifolia, P. meridionalis, P. Mikado, P. recurva, P. rehderiana, P. shensiensis, P. silvestrii, P. taiwaniana, P. thyrsoidea, P. tomentosa, P. viscose.
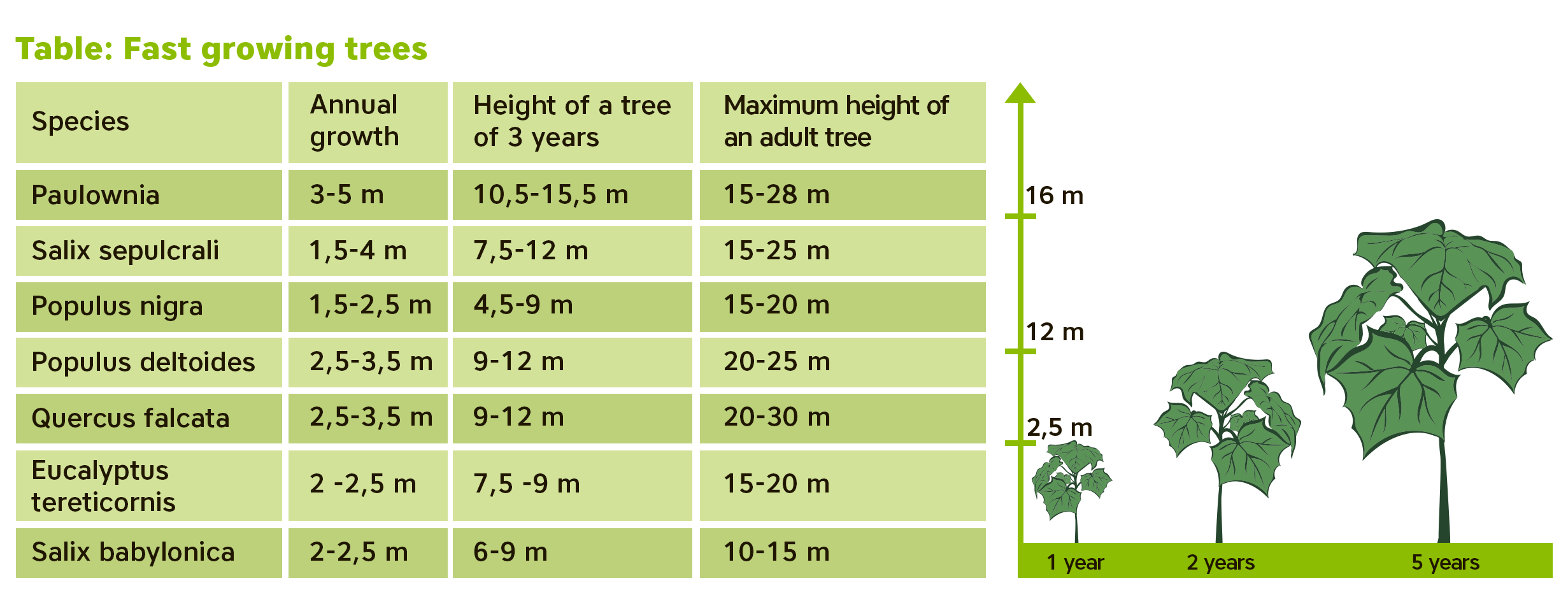
Paulownia is a tree with beautiful large leaves (diameter about 70 cm), flowers (up to 6 cm in diameter) and a beautiful crown. The diameter of the trunk reaches 1 meter. Depending on the growth environment, trees can reach different heights, up to a maximum of 30 meters. It is unpretentious to the soil, this tree grows on any soil, even on dry soils containing up to 2% lime, but it reaches its best development on a deep, moderately moist, drained, fairly fertile, clay soils. This tree is light-loving, and thus it prefers open and well-lit areas. It can be formed in the form of a large multi-stem bush.
Growth rates: The most intensive growth of the Paulownia tree is observed in the first years of life. With age (starting from the 5th year), the growth slows down, and the trunk diameter increases by 1 cm annually. The width and shape of the crown: 3-6 meters, sprawling and widely rounded.
Comparison of fast-growing trees
Regeneration of a tree
Paulownia’s uniqueness lies in the fact that the tree does not require re-planting. After each cutting, clipping, the tree regenerates. The life span of the root is 70-100 years and it can endure between 4 and 8-9 cycles for eight years, which gives us the opportunity to resume our work process without the cost of new planting and land cultivation! The trunk can be cut down at any time of the year, despite the season and short harvesting times, which is not the case with other species of trees.
Foliage: Features of the plant: in the first year of life, the tree has large fibrous leaves, which can reach 50-85 cm in diameter. The leaves are heart-shaped or ovate with round edges, bright green, fluffy from above, and tomentose from below. Color is of the autumn foliage: it does not change. The leaves drop off when they are green, then they turn brown.
Flowering: The flowering of Paulownia comes at spring and lasts for 6-8 weeks, which makes the Paulownia tree an ideal material for the greening of cities and park areas. The flowers are large. Their color is bluish-violet, lilac or almost white. The flowers are collected in large apical panicles.
Root system: tap-root system (anchor) root system. The root reaches a depth of 4.5-9 m.
Bark: Thin-plate, light gray, smooth, with slight cracks in adult trees.
The diameter of the trunk: the circumference of a 1.5-2-year-old tree is 8-14 cm, the circumference of a 3-4 year-old tree is 20-24 cm, and the circumference of an adult 18-year-old tree is up to 80 cm.
Fruits: Long, hooked wood capsules up to 10 mm in size.
Seeds: Butterfly-shaped, 2-7 mm long, membranous, winged.
Pests: Wood of Paulownia accumulates the substance of tannin, which makes it resistant to eating by termites and wood fretters. Paulownia feels good in urban conditions.
Drought and heat tolerance: Paulownia requires regular watering during only the first two years. Water consumption per one seedling is 30-40L contributed 1-2 times a week. After the development of the root system (the third year), the requirements for special watering fall off.
Paulownia is a tree adaptable to the terrain, it is weather resistant, it recovers and regenerates the soil, very decorative and beautiful, environmentally non-aggressive planting, as well as it is an oxygen manufacture and a weapon against global warming, it is a producer of cellulose, fodder and excellent nectariferous plant, while Paulownia is growing rapidly and gaining weight. Paulownia has all properties and qualities that we can use: might and beauty, wood, leaves, flowers!!!
Growth in the size of 1 cubic meter for 7-8 years is incomparable with the growth of any other tree species. The plant as a whole, with its accelerated growth, is a small treasure for humanity: it heals and regenerates soils from erosion, one tree absorbs 22 kg of CO2 and gives 6 kg of oxygen, only think about these figures!
Prepared, quality seedlings of the Paulownia tree with a strengthened root system are able to grow on infertile soils, including clay soils.
Huge leaves and a large crown provide a thick, dense shadow in resting places, parks and squares, forming pleasant cool parts in the center of the gassy and stuffy cities. If there is a tree about which you can say “urban lungs”, this is Paulownia.
Leaves (foliage mass) of Paulownia are often used for fattening of cattle (cows, sheep, goats, etc.) The qualities of Paulownia are close to the qualities of alfalfa. It contains about 20% of the proteins in the green state and about 12% after the fall foliage. It is saturated with microelements; its digestibility is 60%. The highest percentage of protein content is found in annual plants. Therefore, if the main purpose is to obtain nutrient biomass from Paulownia for the fattening of cattle, it is advisable to create a separate plantation and harvest a quality crop at the end of the summer period. Technologies of plantation growing of fast-growing Paulownia trees for production of plant biomass for 1 year on an area of 1 hectare will allow receiving 35-40 tons of quality plant raw materials. Availability and high yield provide low prime cost for fattening – one of the most important indicators when choosing fodder in the industrial livestock production.
It is established that the leaves of Paulownia contain substances that have beneficial effects on the liver, kidney and gallbladder, and the leaves of Paulownia are also used for problems with the lungs. In China, the properties of the leaves of Paulownia have been known for a long time, even the pharmaceutical industry is involved in the industrial production of Paulownia-based medicines. Leaves of Paulownia have other properties: their use in cosmetics in Asian countries is as old as their application in medicine, but it is a novelty for Europe. Only in recent years, extracts from the leaves of Paulownia are included in the composition of medicines, creams and perfumes
Awakening from winter hibernation in February and March, Paulownia grows flowers in the form of a bell, each up to 6 cm in diameter, fleecy, bluish violet, lilac or almost white. The aroma (notes) of flowers of Paulownia is defined as vanilla, powdery and slightly almond. It is established that this is due to the heliotropin substance contained in the aroma known in perfumery and present in other flavors (e.g. Tahitian vanilla). The aroma of flowering Paulownia is analyzed by the so-called “GC mass spec” (Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry) method, based on gas chromatography and mass spectrometry.
In addition to beauty, the flowers of Paulownia are also distinguished by strong, fragrant aroma and they are an excellent nectariferous plants! From one hectare of Paulownia it is possible to receive 800 kg and more honey. The advantage is that when growing Paulownia tree, the chemical products are not used at all, so we do not harm bees that do not tolerate the use of herbicides and other chemicals, receiving a NATURAL (ECOLOGICALLY CLEAN) product. Honey from Paulownia is light, transparent, very bright and fragrant. Honey frm Paulownia can be compared only with honey from acacia by its color and consistency. Honey from Paulownia, as well as acacia, is of the highest quality. In addition to being a delicacy, it also serves as a medicine. Its properties are known as such that have beneficial effects and help in the treatment of bronchitis, lungs and respiratory system diseases, and Paulownia also improves the function of the gallbladder, liver and digestion in general. The qualities of Paulownia honey are determined by biologically active substances in its flowers, so that flowers themselves are used for food.
In addition to the Chinese experience in this respect, we cannot miss the fashionable use of Paulownia’s flowers in the form of horns with cream – it can sound like an exotic dessert, but it is already a part of the menu of many European restaurants.
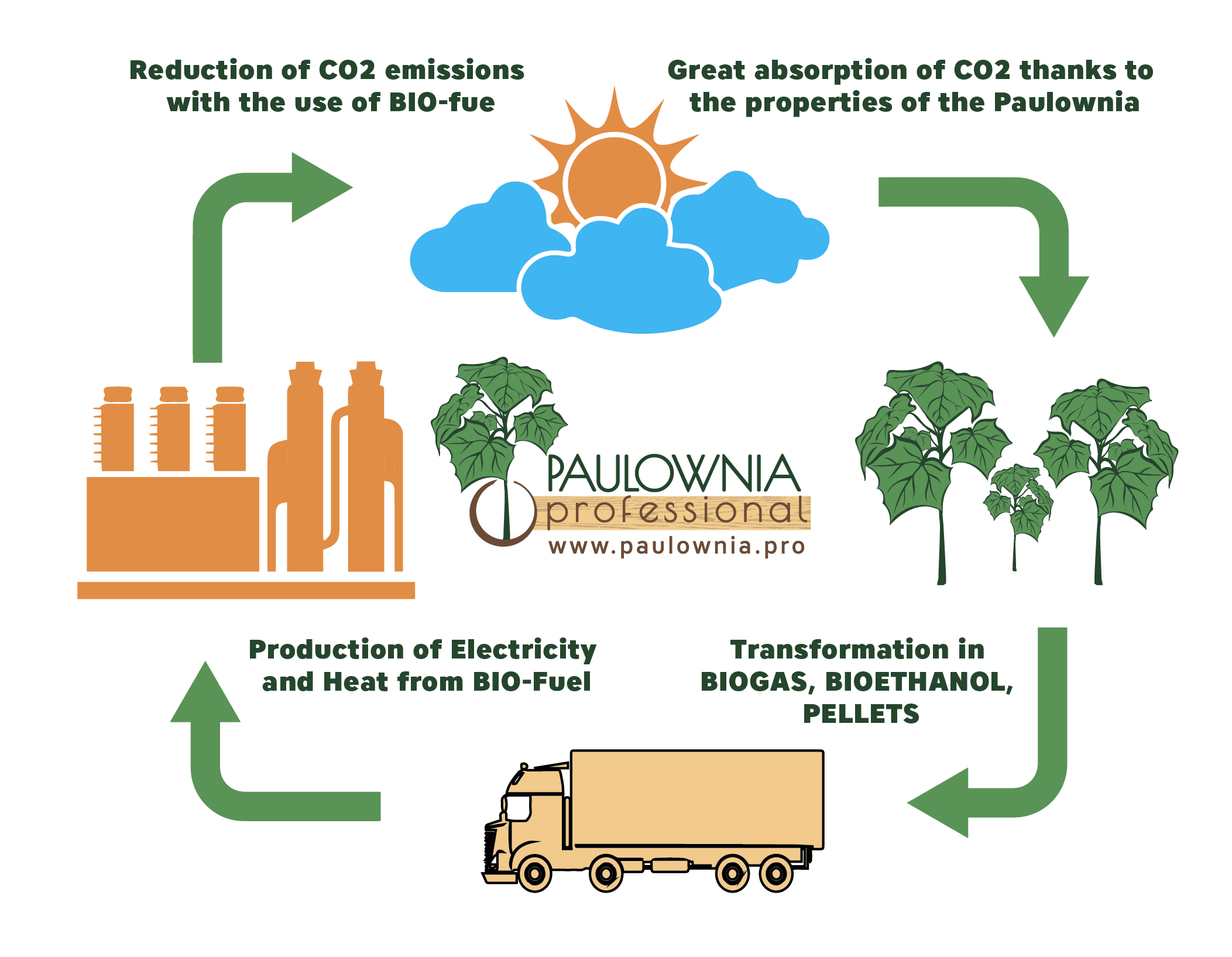 The leaves of Paulownia are increasingly being used as a component of the organic matter of this biofuel. Having a large size, at decomposition more basic gases are produced, of which biogas is directly composed, compared to the organic material offered by other types of plants, making Paulownia an ideal product for obtaining this biofuel.
Another application of Paulownia is its use as raw material for the production of Bioethanol. American scientists have developed a new technology based on the combination of thermochemical and biotechnological methods resulting in the extraction of 511 liters of ethanol from one ton of dry wood. This is the only reason to call our tree an “oil well”.
The creation of plantations of fast-growing trees, combined with the innovative technologies for growing Paulownia trees can become an important part of the policy of saving resources and solving problems related to energy consumption, without risk to the environment.
The leaves of Paulownia are increasingly being used as a component of the organic matter of this biofuel. Having a large size, at decomposition more basic gases are produced, of which biogas is directly composed, compared to the organic material offered by other types of plants, making Paulownia an ideal product for obtaining this biofuel.
Another application of Paulownia is its use as raw material for the production of Bioethanol. American scientists have developed a new technology based on the combination of thermochemical and biotechnological methods resulting in the extraction of 511 liters of ethanol from one ton of dry wood. This is the only reason to call our tree an “oil well”.
The creation of plantations of fast-growing trees, combined with the innovative technologies for growing Paulownia trees can become an important part of the policy of saving resources and solving problems related to energy consumption, without risk to the environment.
CONCLUSION
All kinds of Paulownia cultivated for commercial purposes are clones. This means that they are identical plants with the specific characteristics. The most used species in the wood industry are hybrids based on Paulownia Fortunei and Tomentosa, as the former species is endowed with the properties of rapid growth and high-quality wood, and the second species is known for its tolerance to cold and it can develop in places where winter temperatures reach -10º C or even lower. Also on a par with them, the Paulownia Elongata and its hybrids are used. This species also gives excellent results, but you need to take into account the fact, that it is thermophilic species. Therefore, we want to focus your attention on the fact that species are very different in characteristics and resistance to weather conditions and you need to approach the choice of planting material very carefully! To date, the market has a wide range of species of various hybrids of Paulownia intended for the cultivation of quality wood. Our Paulownia Professional Company is ready to help you decide on a choice by offering only leading and decades-proven species and their selection.